
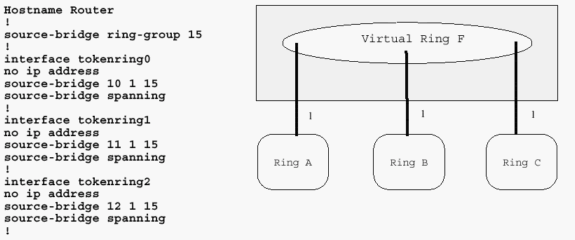
If a station has data to transmit when it receives a token, it sends the data and then passes the token to the next station otherwise, it simply passes the token to the next station. Token Passing Mechanism in Token BusĪ token is a small message that circulates among the stations of a computer network providing permission to the stations for transmission. The working principle of token bus is similar to Token Ring. A station can only transmit data when it has the token. Each node knows the address of its preceding station and its succeeding station. A virtual ring is created with the nodes/stations and the token is passed from one node to the next in a sequence along this virtual ring. The physical media has a bus or a tree topology and uses coaxial cables. Token Bus (IEEE 802.4) is a standard for implementing token ring over virtual ring in LANs. In order that tokens are not circulated infinitely, they are removed from the network once their purpose is completed. The data flow is unidirectional in the direction of the token passing. Passing the token means receiving the token from the preceding station and transmitting to the successor station. If a station has a frame to transmit when it receives a token, it sends the frame and then passes the token to the next station otherwise it simply passes the token to the next station. The tokens are released on successful receipt of the data frame.

A station can send data frames only if it holds a token. A token is a special frame of 3 bytes that circulates along the ring of stations. Token ring (IEEE 802.5) is a communication protocol in a local area network (LAN) where all stations are connected in a ring topology and pass one or more tokens for channel acquisition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
